Uncontrolled inflammation is associated with the pathophysiology of numerous diseases. The hyperinflammatory conditions are often accompanied with multi-organ system failure that correlates with a high mortality. Currently, there has been no effective approaches for addressing this clinical unmet need. It is well believed that there exists a positive feedback loop between pro-inflammatory signaling and redox imbalance in cells during the progression of uncontrolled inflammation. It has been recently revealed that ferroptosis is highly involved in such loop and ferroptosis inhibition appears as a novel means for efficient management of uncontrolled inflammation. Ferroptosis is ferrous ion-dependent, regulated cell death pathway that is driven by the peroxidation of tailored lipids in cell membranes. Lipid radical trapping is a standard approach for suppressing ferroptosis. However, the currently available small molecule radical trapping agent shows multiple limits, such as limited aqueous solubility and poor in vivo pharmacokinetics. Inspired by the structure of cell membrane that consists of phospholipids and different proteins (e.g. alpha-helix proteins), the Zhao and Wang Group at SPST proposed a self-assembling polymer-drug conjugate for efficient ferroptosis inhibition. The amphiphilic conjugate contains a hydrophilic methoxyl poly(ethylene glycol)/mPEG block and a multivalent polylysine (PLys) block that covalently links with a model ferroptosis inhibitor that is the derivative of Fer-1. The hydrophobic block of tailored polymers adopts an alpha-helix conformation for prolonged cell membrane retention, and thus competent alleviation of hyperinflammation. The tailored anti-ferroptotic micelles could efficiently mitigate the intracellular inflammatory cytokines in lipopolysaccharide-incubated macrophages, which was in line with the superior in vivo efficacy in lipopolysaccharide-triggered mice model. This work provides a translational nanomedicine for efficient management of uncontrolled inflammation.
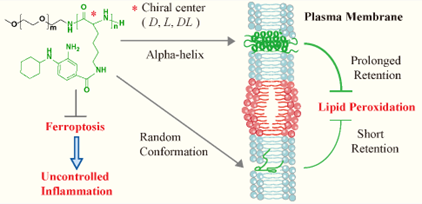
Fig 1. Radical trapping chiral polymers for prolonged membrane retention, and enhanced inhibition of ferroptosis and uncontrolled inflammation.

